The foundry industry relies heavily on the use of refractory materials in various stages of metal casting. Refractories are materials that can withstand extremely high temperatures while providing thermal insulation and maintaining their structural integrity. In foundries, these materials are used to line furnaces, ladles, and other equipment that come into contact with molten metal.
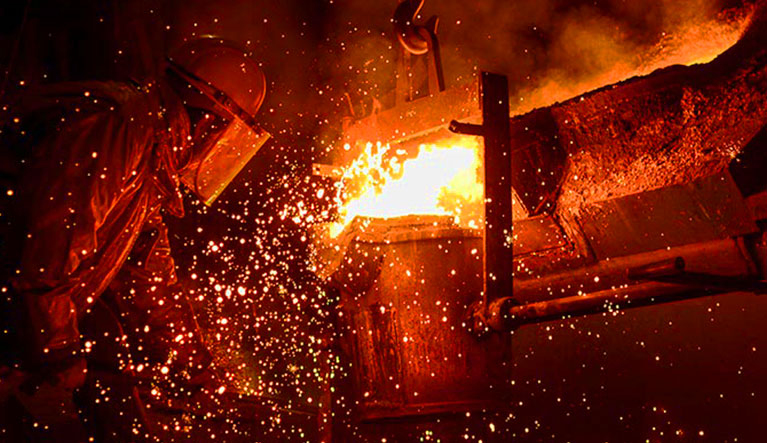

Melting furnaces: Refractory materials line the interiors of melting furnaces, such as cupolas and induction furnaces, where they protect the furnace shell from molten metal, preventing heat loss and prolonging furnace life.
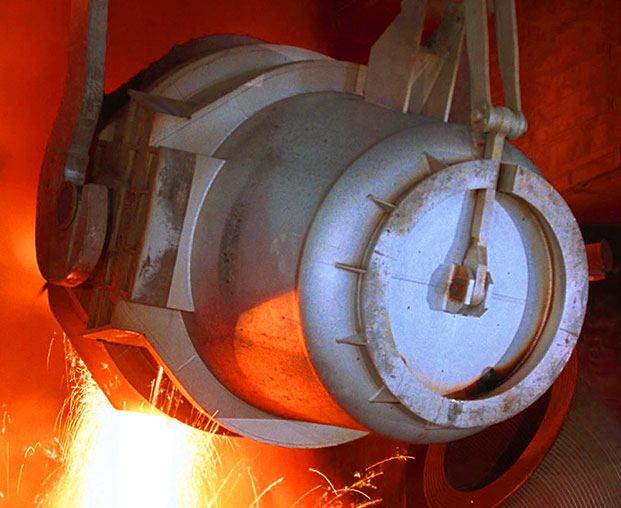
Ladles: Molten metal is transferred from furnaces to molds using refractory-lined ladles. The refractory lining ensures the metal stays at the desired temperature and prevents contamination from the environment.
Molds and cores: Refractory materials are often used in the production of sand molds and cores, which are essential for creating complex metal castings. The high-temperature resistance of refractories ensures that molds maintain their shape and dimensional accuracy during metal pouring.
Hot blast stoves: In the blast furnace process, hot blast stoves preheat air blown into the furnace to increase smelting efficiency. Refractory materials line these stoves to withstand high temperatures and provide insulation.
Improve efficiency: Refractory materials enable better heat containment, reducing energy consumption and increasing production efficiency.
Extend equipment life: Refractory linings protect foundry equipment from wear and tear caused by high temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion, extending their service life.
Senhance Product Quality: Refractory materials prevent contamination from the environment, ensuring the purity of molten metal and improving the quality of final castings.
In conclusion, refractory materials are indispensable in the foundry industry, playing a critical role in metal casting processes. Their unique properties enable improved efficiency, enhanced metal quality, and extended equipment life, making them an essential component of modern foundry operations.
The foundry industry relies heavily on the use of refractory materials in various stages of metal casting.